How to Deploy Laravel on AWS Elastic Beanstalk
Sagar J.
Oct 29, 2025
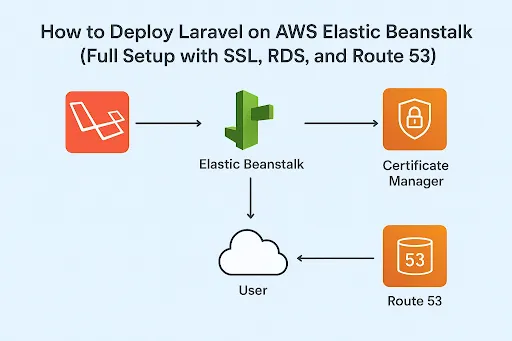
Deploying Laravel on AWS might sound complex, but with AWS Elastic Beanstalk, it becomes smooth and automated. You can deploy your app, connect a managed database, secure it with SSL, and configure your custom domain — all from AWS’s intuitive web interface.
In this article, we’ll walk through the full Laravel deployment setup — covering Elastic Beanstalk, RDS, Certificate Manager, Load Balancer, and Route 53.
No terminal commands, just form-based configuration and a ZIP upload.
What Is AWS Elastic Beanstalk?
Elastic Beanstalk (EBS) is a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) that automates application deployment and management. It supports several languages and frameworks, including PHP — making it perfect for Laravel.
Why Use Elastic Beanstalk for Laravel?
- Automatic server provisioning, load balancing, and auto-scaling.
- Built-in monitoring, logging, and health checks.
- Easy integration with RDS, S3, and CloudWatch.
- Simple ZIP upload for deployment — no CLI required.
- No additional cost for Beanstalk — you only pay for underlying AWS resources like EC2 and RDS.
Explore Elastic Beanstalk: aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk
AWS Services Overview
Here’s what we’ll use and why each service matters:
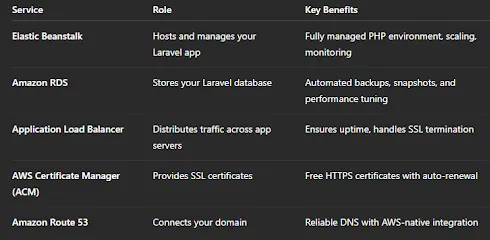
Why Each Service Matters
-
RDS (Relational Database Service) — Provides a managed MySQL or PostgreSQL database. AWS automatically handles backups, replication, and scaling so you can focus on your app.
Learn more about RDS
-
AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) — Lets you create and manage SSL/TLS certificates for your domain for free. Certificates are easy to attach to your Load Balancer and auto-renew.
Learn more about ACM
-
Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) — Distributes web traffic to ensure high performance and availability. It’s also where your SSL certificate is applied.
Learn more about Load Balancing
-
Route 53 — Handles DNS management for your custom domain (like myapp.com). It’s globally reliable and integrates seamlessly with ACM and Beanstalk.
Learn more about Route 53
Step-by-Step Laravel Deployment Guide
Step 1: Prepare Your Laravel App
Before you upload your app:
1. Set APP_ENV=production and APP_DEBUG=false in .env
2. Run composer install --optimize-autoloader --no-dev locally.
3. Include your /vendor folder in the project.
4. Zip your entire Laravel project folder — including /app, /public, /vendor, .env.example, and other required files.
💡 Tip: Your ZIP should look exactly like the folder structure Laravel expects in production.
Step 2: Create an Elastic Beanstalk Environment
1. Go to AWS Console → Elastic Beanstalk → Create Application.
2. Choose:
— Platform: PHP
— Environment type: Web server environment
3. Upload your Laravel .zip file.
4. Click Create Environment.
- Launch EC2 instances
- Configure PHP-FPM and Nginx automatically
- Create and attach a Load Balancer
- Deploy your app
You’ll receive a default Beanstalk URL, e.g.
https://myapp.us-east-1.elasticbeanstalk.com Step 3: Set Up a Managed Database (RDS)
1. Go to AWS Console → RDS → Create Database.
2. Select MySQL (or PostgreSQL).
3. Choose a Free Tier instance type (e.g. db.t3.micro).
4. Provide your database name, username, and password.
5. Make sure to select the same VPC as your Beanstalk app.
Once created, note the RDS endpoint, e.g.mydb.xxxxx.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com
Next, go to Elastic Beanstalk → Configuration → Software and set these Environment Properties:
Beanstalk will inject these automatically into your Laravel environment.
Step 4: Secure Your App with SSL (AWS Certificate Manager)
1. Navigate to AWS Certificate Manager (ACM).
2. Click Request a Certificate → Public Certificate.
3. Add your domain (example.com and www.example.com).
4. Choose DNS Validation (if using Route 53, AWS will create the record automatically).
5. Wait for the certificate status to show Issued.
✅ ACM certificates are free, auto-renewing, and integrate directly with Load Balancers.
Step 5: Enable HTTPS on Your Load Balancer
1. Go to Elastic Beanstalk → Configuration → Load Balancer.
2. Under Listeners, add a new listener for HTTPS (port 443).
3. Attach your newly issued ACM certificate.
4. Optionally, redirect all HTTP (port 80) traffic to HTTPS in .htaccess or via Load Balancer rules.
Your Laravel app now supports secure HTTPS connections.
Step 6: Connect Your Domain via Route 53
1. Go to Route 53 → Hosted Zones → Create Record.
2. Create an A Record (Alias).
3. Select Alias to Elastic Beanstalk Environment and choose your region and environment.
Your custom domain (e.g. myapp.com) now points to your Beanstalk-hosted Laravel app — with full SSL.
Important: Review AWS Pricing
Before going live, always review AWS pricing to avoid unexpected charges.Each service (EC2, RDS, Route 53, Load Balancer, etc.) has its own pricing model.
Check Pricing:
- Elastic Beanstalk → aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/pricing
- RDS → aws.amazon.com/rds/pricing
- Route 53 → aws.amazon.com/route53/pricing
- ACM → aws.amazon.com/certificate-manager/pricing
- Load Balancer → aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/pricing
Always double-check your selected region and instance types — pricing can vary.
Final Thoughts
By combining Elastic Beanstalk, RDS, ACM, and Route 53, you get a production-ready Laravel environment that’s:
- Scalable (auto-scaling based on load)
- Secure (SSL-enabled via ACM)
- Reliable (backed by AWS-managed resources)
- Simple to maintain (no server management required)
This architecture allows you to focus on your Laravel app instead of DevOps setup — ideal for startups, agencies, or solo developers.
