How to Use One Load Balancer for Multiple Elastic Beanstalk Environments (Production + Sandbox)
Sagar J.
Nov 25, 2025
When working with multiple AWS Elastic Beanstalk environments (Production, Staging, Sandbox), the monthly cost can rise quickly — mainly because each environment spins up its own Application Load Balancer (ALB).
But what if you could run both Production and Sandbox behind a single ALB?
Spoiler: Yes, you can.
And this can save $300+ per year — per environment.
This guide covers:
1. Why sharing an ALB makes sense
2. Architecture overview
3. Step-by-step configuration
4. Using AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) for HTTPS
5. Cost savings
6. Common pitfalls
Let’s dive in.
Why Share One Load Balancer?
By default, Elastic Beanstalk creates one ALB per environment.
Each ALB typically costs:
- $20–$30/month, depending on traffic + hours
- Extra cost for SSL certificates (if using third-party)
If your Sandbox or Staging environment doesn’t need high scalability, you can:
- Keep Production behind ALB
- Run Sandbox as a Single Instance (no ALB)
- Attach Sandbox manually to Production ALB using rules
Benefits
- Save $300+ annually
- One centralized SSL configuration
- Domain-based routing (e.g., sandbox.example.com)
- Cleaner infrastructure
- Fewer AWS resources to manage
Architecture Overview
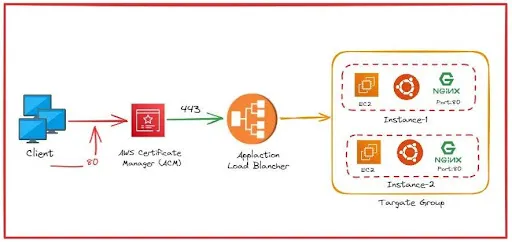
We will configure:
- Production EB → ALB manages it (default EB architecture)
- Sandbox EB → Single EC2 instance (no ALB)
- A single ALB → Routes based on domain
- ACM Certificate → Valid for both Production & Sandbox
Step-by-Step Setup Guide
Step 1: Create the Sandbox Environment (Single Instance)
In Elastic Beanstalk:
- 1. Create a new environment
- 2. Choose Web Server Environment
- 3. Under Load Balancer Type, select: Single Instance (No Load Balancer)
- 4. Deploy your app normally
This gives a cost-efficient sandbox with only 1 EC2 instance.
Step 2: Create a Target Group for Sandbox
Since Sandbox has no ALB, EB will not create a Target Group.
You must create it manually.
- 1. Go to EC2 → Target Groups
- 2. Create Target Group
- Target type: Instance
- Protocol: HTTP
- 3. Register the Sandbox EC2 instance
- 4. Ensure health checks return 200 OK
Step 3: Add Domain Routing Rules to ALB
You do not need a new 443 listener.
Use the existing one from Production.
- 1. Open EC2 → Load Balancers
- 2. Select the Production ALB
- 3. Go to Listeners → HTTPS (443)
- 4. Click Add Rule
- 5. Create rule:
IF Host header = sandbox.example.com
THEN Forward → SANDBOX TARGET GROUP
Step 4: Add DNS Record for Sandbox Domain
In Route53:
Create CNAME:
sandbox.example.com →your-ALB-dns-name.amazonaws.com
ALB will route the traffic.
Using AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) for HTTPS
ACM certificates cannot be installed on EC2 instances or Single Instance EB.
They only work with:
- ALB
- NLB
- CloudFront
- API Gateway
So the ALB will handle all HTTPS termination.
Step 1: Request a Certificate in ACM
Request a new Public Certificate.
Add domains:
- example.com
- *.example.com (recommended!)
Validate using DNS CNAME.
Step 2: Attach Certificate to ALB Listener
- Open ALB → Listeners
- Choose HTTPS (443)
- Add → ACM Certificate
Now HTTPS works for all domains pointing to ALB.
Step 3: Optional — Redirect HTTP → HTTPS
Add rule:
At your backend:
IF protocol = HTTP→
THEN RedirectHTTPS
Cost Benefits
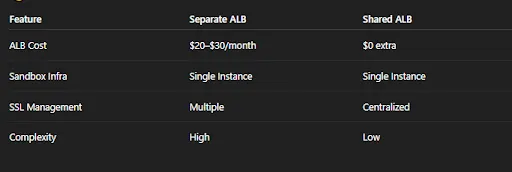
Total Savings
~$300/year per environment
Common Pitfalls & Fixes
ALB Health Checks Failing
Allow ALB Security Group → Sandbox EC2 instance
SSL Not Working for Sandbox
Add sandbox.example.com to the ACM certificate
Routing Goes to Production
Increase Sandbox rule priority
Sandbox Not Reachable
Ensure EC2 instance is in a public subnet
Real Issue We Faced: Sandbox Instance Not Attaching to Target Group
When using a Single Instance Elastic Beanstalk Sandbox, we discovered a major issue:
If the EC2 instance becomes degraded and EB replaces it, the new instance does NOT automatically attach to the custom target group.
Why? Because the target group was created manually.
EB only auto-registers instances for EB-managed ALBs, not for manually created ones.
What happened:
- 1. Sandbox instance became unhealthy
- 2. EB created a new instance
- 3. New instance was NOT registered to the target group
- 4. ALB had zero healthy targets
- 5. Sandbox became inaccessible
This is a frequent and often overlooked issue in this architecture.
Solution: Auto-Register Sandbox EC2 Instances Using a Post-Deploy Hook
Instead of using Lambda/EventBridge, we applied a simpler solution inside the EB environment itself, using a post-deploy hook that runs every time EB launches or replaces an instance.
- No Lambda
- No cost
- Simple
- Runs automatically on every new EC2 instance
How the Fix Works
We created:
.platform/hooks/postdeploy/01-register-target.sh
This script:
- Retrieves the EC2 instance ID (IMDSv2)
- Checks whether it’s already attached
- If not attached → registers it into the sandbox target group
Full Script
Required IAM Permissions
To allow the script to interact with ELB, we added an inline policy to the:
aws-elasticbeanstalk-ec2-service-role
Inline IAM Policy
After adding the policy, we redeployed the environment so a new instance picked up the updated role.
Outcome
With this fix:
- Every new Sandbox EC2 instance auto-registers to the custom target group
- No downtime when EB replaces the instance
- No manual intervention needed
- The overall architecture stays clean and cost-efficient
This makes the shared ALB setup fully stable for Sandbox workflows.
Final Thoughts
Using one Application Load Balancer for multiple Elastic Beanstalk environments is one of the most effective AWS cost-saving designs — while maintaining full HTTPS support via ACM.
You get:
- Centralized SSL
- Domain-based routing
- Secure sandbox environments
- Lower AWS bill
- Cleaner architecture
If you’re running multiple EB environments, this setup is a must-implement architecture.
Important Note (Please Read Before Implementation)
Before you apply this architecture, please remember:
-
Every AWS setup is different.
The steps in this guide are based on common AWS best practices, but your VPC, security groups, subnets, routing, and Elastic Beanstalk configuration may vary. - Please perform your own R&D and test everything in a Sandbox environment first before implementing it in Production. Validate the ALB listener rules, target group health checks, SSL behavior, and DNS routing to ensure it works correctly in your environment.
