Using n8n as a Backend Scheduler and Notification Engine with Laravel
Shrestha N.
Jan 13, 2026

n8n is often associated with no-code automation — email campaigns, CRM syncing, or social media posting. Because of that, it’s frequently dismissed as a tool for non-technical users.
In practice, we’ve found n8n to be highly effective in a professional engineering environment, where it operates as a scheduler, event listener, and notification engine alongside backend systems such as Laravel.
Rather than embedding time-based logic, notifications, and integration code deep into the backend, n8n acts as an automation layer: handling scheduling, reacting to events, and delivering notifications with strong observability and minimal operational overhead.
This article outlines how we use n8n beyond marketing automation — as a maintainable, production-ready component of our backend architecture.
Why Use n8n in a Backend Architecture?
In traditional backend systems, automation is usually handled by:
- Cron jobs
- Queue workers
- Background services
- Custom scripts
While these approaches work, they tend to degrade over time — especially as teams and systems grow. Automation logic becomes scattered across cron definitions, queue workers, and custom scripts, making it harder to reason about what runs when, why it failed, and who owns it.
n8n helps solve this by providing:
- Visual workflows with execution history
- Built-in schedulers (cron-like)
- Webhooks for real-time events
- Database triggers
- Retry logic and error handling
This makes it suitable as an automation and orchestration layer, rather than a replacement for the backend.
1. Scheduler Trigger: Replacing Traditional Cron Jobs
The Scheduler Trigger in n8n works like a cron job but without server-level configuration.
Common office use cases:
- Daily or weekly notification emails
- Scheduled reports
- Trial or subscription reminders
- Periodic data sync tasks
An important side effect of this approach is organizational safety. Scheduling logic becomes visible and adjustable without direct server access, reducing the risk of accidental misconfiguration and removing routine changes from the deployment pipeline.
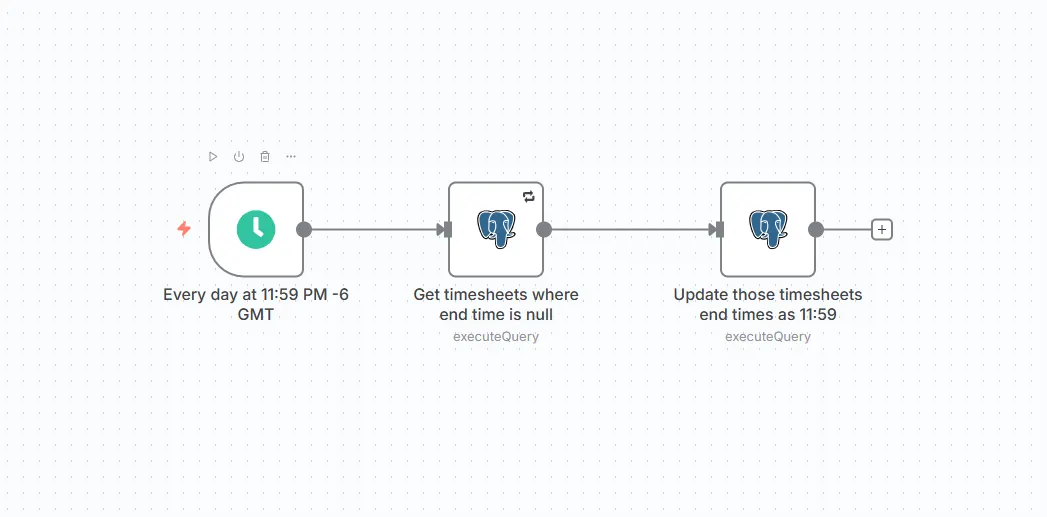
Instead of editing crontab entries or Laravel scheduler files, schedules can be managed directly in n8n. This allows both developers and operations teams to adjust automation timing safely and quickly.
2. Database Trigger: Reacting to Data Changes
n8n also supports Database Triggers, which can listen for changes such as:
- New records are being inserted
- Status updates
- Field value changes
This is useful for automation scenarios where actions must happen immediately after a database change — for example, sending notifications when a status becomes “approved” or “completed”.
That said, in more complex systems, directly exposing the database is not always preferred.
3. Webhook Trigger: Event-Driven Automation (Preferred Approach)
In our setup, the Webhook Trigger is used more frequently than database triggers.
Why?
- Backend controls validation and authorization
- No direct database access required
- Faster and more predictable
- Fits well with event-driven architectures
The backend (Laravel) emits events via HTTP requests, and n8n handles the automation steps, such as notifications, emails, or third-party integrations.
In practice, webhooks give us a clean architectural boundary: the backend owns state and intent, while n8n reacts to well-defined events.
Example: Shift Accepted → Send Confirmation Email
Scenario
When a worker accepts a shift:
- 1. Laravel updates the shift status
- 2. A webhook is triggered
- 3. n8n sends a confirmation email to the worker
Step 1: Laravel — Trigger Webhook After Shift Acceptance
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Http;
public function acceptShift( Shift $shift)
{
$shift->update([
'status'=>'accepted',
]);
Http::post (config('services.n8n.shift_webhook'), [
'shift_id'=>$shift->id,
'worker_email'=>$shift->worker->email,
'worker_name'=>$shift->worker->name,
'shift_date'=>$shift->date,
'start_time'=>$shift->start_time,
'end_time'=>$shift->end_time,
]);
}
In production, this request is wrapped with basic retry and timeout handling, and failures are logged without blocking the main business flow.
This logic can also be placed inside a Laravel Job so it runs asynchronously.
Step 2: n8n Workflow
Workflow structure:
Webhook Trigger
↓
Set / Format Data
↓
Send Email
Webhook Trigger
-
Method:
POST -
Path:
/shift-accepted
n8n receives the payload from Laravel.
Send Email Node
Example email content:
Subject: Shift Confirmation
Hello {{worker_name}},
Your shift on {{shift_date}} from {{start_time}} to {{end_time}} has been successfully confirmed.
Thank you.
This email can be sent via:
- SMTP
- Gmail
- Outlook
- Any supported email service
Why This Approach Works Well in Production
Using n8n this way provides several advantages:
Clear separation of responsibilities
- Laravel/Backend systemhandles business rules and data integrity
- n8n handles automation and notifications
Reduced backend complexity
- Fewer cron jobs
- Less custom notification logic
- Easier debugging through n8n execution logs
Operational visibility
- Every workflow execution is logged
- Failed executions can be retried
- No need to dig through server logs
Scalable automation
- New notifications or workflows can be added without redeploying backend code
Typical Office Use Cases
In a professional environment, n8n can be used for:
- Shift and task notifications
- Status-based emails
- Scheduled reminders
- Internal alerts
- Integration with third-party tools
- Automation of repetitive operational processes
Conclusion
While n8n is widely known for email and social media automation, it also works extremely well as a backend-facing automation layer.
By combining scheduler triggers, webhook-driven events, and a conventional backend (such as Laravel), teams can build automation that is observable, flexible, and easier to evolve over time — without overloading the core application.
n8n fits best not as a replacement for backend systems, but as a powerful companion that absorbs operational complexity and keeps automation visible.
