A Practical Guide to Soketi for Developers
Sagar J.
Jan 01, 2026

Real-time communication powers many modern applications — live bookings, chat systems, notifications, dashboards, delivery tracking, and more.
While many teams start with hosted services like Pusher, these solutions often become expensive, opaque, and limiting as applications scale.
Soketi is an open-source, Pusher-compatible WebSocket server designed for teams that want performance, control, and predictable costs without sacrificing reliability.
In this guide, we’ll cover:
- Why and when Soketi is a good fit
- How to install and configure it
- Running Soketi with PM2 in production
- Securing it with SSL and Nginx
- Key architectural, R&D, and safety considerations
Official Soketi Documentation Links
Before starting, explore the official documentation:
🔗 Soketi Documentation
https://docs.soketi.app/
🔗 Soketi CLI Installation Guide
https://docs.soketi.app/getting-started/installation/cli-installation
What is Soketi?
Soketi is an open-source WebSocket server that implements the Pusher protocol, allowing teams to run real-time infrastructure without changing existing frontend code.
It is designed to be:
- Fully compatible with Pusher clients
- Lightweight and optimized for high concurrency
- Self-hosted and cost-efficient
- Secure and production-ready
- Easy to integrate into existing stacks
- Capable of scaling with growing workloads
If you’re already using Laravel Echo, Vue, React, Node.js, or any Pusher-compatible client, Soketi can be introduced as a drop-in replacement with minimal friction.
Why Developers Choose Soketi
1. Drop-in Pusher replacement
Soketi works with existing Pusher SDKs, which means no frontend rewrites and no protocol lock-in.
2. Built for performance
Designed to handle high concurrency with low memory overhead, Soketi performs well even on modest infrastructure.
3. Predictable, low infrastructure costs
Instead of per-connection or per-message pricing, a small self-hosted server can handle thousands of concurrent connections.
4. Full ownership and control
Self-hosting gives you visibility into performance, flexibility in scaling, and control over your data.
5. Feature parity and Pusher
Private and presence channels, client events, webhooks, batching, limits, and more are supported out of the box.
6. Production-friendly deployment
Soketi integrates cleanly with PM2 and Nginx, making it suitable for secure, stable production environments.
When Should You Use Soketi?
Soketi is a strong fit for systems that depend on low-latency, real-time updates, such as:
- Chat and messaging platforms
- Real-time notifications
- Live dashboards and monitoring tools
- Booking and delivery systems
- Multiplayer games
- Trading or financial platforms
- IoT and telemetry systems
- Collaborative applications
If your application needs instant updates and you want control over cost, infrastructure, and performance, Soketi is a practical and scalable choice.
Before You Run Soketi in Production
Before deploying Soketi to production, it’s important to treat it like any other critical real-time infrastructure component. The following practices help ensure stability, security, and predictable behavior under load.
1. Validate Everything in a Staging Environment
Never deploy Soketi straight to production.
Make sure you:
- Test event broadcasting end-to-end
- Verify private and presence channel authorization
- Simulate real user behavior
- Load test concurrent connections and message throughput
This helps surface configuration and scaling issues early.
2. Protect Your Application Key
Your Soketi secret must never be exposed to the frontend.
Best practices:
- Store all keys in environment variables
- Keep secrets strictly on the backend
- Rotate keys if exposure is suspected
Leaked keys can compromise your entire real-time layer.
3. Always Use SSL / TLS (WSS)
Unencrypted WebSocket traffic is unsafe in production.
Make sure:
- All connections use HTTPS and WSS
- Certificates are valid and auto-renewed
- Mixed-content issues are eliminated
SSL is non-negotiable for real-time systems.
4. Run Soketi Behind a Reverse Proxy (Nginx)
Using Nginx in front of Soketi enables:
- SSL termination
- Proper WebSocket upgrades
- Rate limiting and basic DDoS protection
- Improved performance and stability
This setup is strongly recommended for production.
5. Use PM2 for Process Management
Soketi should never be running as a raw Node process.
PM2 allows you to:
- Auto-restart on crashes
- Start Soketi on server reboot
- Monitor logs and uptime
This is essential for long-running WebSocket services.
6. Monitor Resource Usage Continuously
Real-time servers are sensitive to load.
Monitor:
- CPU and memory usage
- Number of active WebSocket connections
- Event throughput and spikes
Early visibility prevents outages.
7. Keep Dependencies Updated
Regularly update:
- Node.js
- Soketi
- SSL certificates
- System packages
Security patches and performance improvements matter.
8. Prepare a Rollback Strategy
Always assume something can go wrong.
Recommended:
- Regular server snapshots
- Versioned configuration files
- Clear rollback steps
Fast recovery is just as important as uptime.
Final Note
Following these practices helps ensure your Soketi deployment remains secure, stable, and production-ready, even as traffic and complexity grow.
Primary Architecture
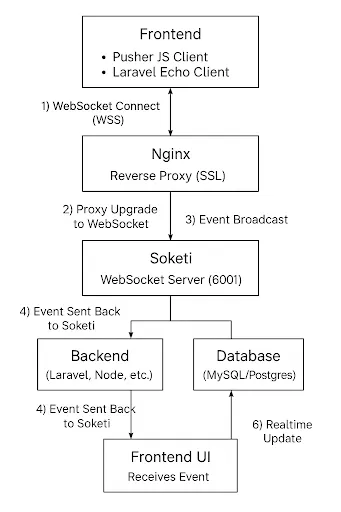
Full Installation Guide: Soketi on Lightsail (Ubuntu + Nginx + SSL + PM2)
Step 1: Install Dependencies
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y git python3 gcc build-essential
Step 2: Install Node.js, Soketi & PM2
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_22.x | sudo -E bash - sudo apt install -y nodejs npm sudo npm install -g @soketi/soketi sudo npm install -g pm2
Step 3: Create Soketi Directory
sudo mkdir -p /opt/bitnami/projects/soketi
cd /opt/bitnami/projects/soketi
Step 4: Create Config File
/opt/bitnami/projects/soketi/soketi-config.json
{
"debug": true,
"port": 6001,
"appManager.array.apps": [
{
"id": "dummy-app-id",
"key": "dummy-app-key",
"secret": "dummy-app-secret",
"enabled": true,
"enableClientMessages": true
}
]
}
Step 5: Create Start Script
start_soketi.sh sudo soketi start - config="/opt/bitnami/projects/soketi/soketi-config.json"
Give permission:
chmod +x start_soketi.sh
Step 6: PM2 Ecosystem File
ecosystem.config.js
module.exports = {
apps: [
{
name: "soketi-server",
script: "./start_soketi.sh",
instances: 1,
autorestart: true,
watch: false,
max_memory_restart: "250M",
exec_mode: "fork"
}
]
};
Start PM2:
pm2 start ecosystem.config.js pm2 save pm2 startup
Why PM2 Is Essential in Production
Soketi is a long-running WebSocket service. Running it as a plain Node.js process is risky in production.
PM2 provides:
- Automatic restarts if the process crashes
- Automatic startup after server reboots
- Centralized logs and memory monitoring
- Clean process management for long-running services
Without a process manager like PM2, your WebSocket server can silently stop, leading to dropped connections and degraded real-time features.
For production environments, PM2 is not optional — it’s a baseline requirement.
Step 7: Securing Soketi with SSL (WSS)
All production WebSocket traffic should be encrypted.
SSL is required to:
-
Enable secure
wss://connections - Protect real-time data in transit
- Prevent browser security warnings and blocked connections
Depending on your hosting setup, SSL can be configured using:
- Certbot (Let’s Encrypt)
- Built-in SSL support from managed platforms like Bitnami
- Cloud provider solutions such as AWS Lightsail HTTPS
Once SSL is enabled, Soketi can safely handle secure WebSocket connections behind Nginx.
Step 8: Configure Nginx Reverse Proxy
Open :
/opt/bitnami/nginx/conf/server_blocks/default-https-server-block.conf
Add:
server {
listen 443 ssl;
ssl_certificate /opt/bitnami/nginx/conf/example.com.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /opt/bitnami/nginx/conf/example.com.key;
include "/opt/bitnami/nginx/conf/bitnami/*.conf";
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:6001;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_read_timeout 60;
proxy_connect_timeout 60;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
}
}
Restart Nginx:
sudo /opt/bitnami/ctlscript.sh restart
Step 9: Test Soketi Connection
<script src="https://js.pusher.com/8.2.0/pusher.min.js"></script>
<script>
Pusher.logToConsole = true;
const pusher = new Pusher("dummy-app-key", {
wsHost: "ws.example.com",
wsPort: 443,
forceTLS: true,
disableStats: true
});
</script>
Step 10: Test Event Listening
<script>
var pusher = new Pusher("dummy-app-key", {
wsHost: "ws.example.com",
forceTLS: true
});
var channel = pusher.subscribe("booking.123");
channel.bind("booking.updated", function(data) {
console.log("Event Received:", data);
});
</script>
Conclusion: Is Soketi Right for Your Real-Time Stack?
Soketi offers a compelling alternative to managed real-time services by combining Pusher compatibility, high performance, and predictable infrastructure costs — without sacrificing production stability.
When deployed correctly with PM2, SSL, and Nginx, and supported by solid operational practices, Soketi becomes a reliable WebSocket layer capable of handling demanding real-time workloads at scale.
For teams that want control over their real-time infrastructure — and are willing to operate it responsibly — Soketi is not just a replacement for Pusher, but a long-term, production-ready solution.
